Emergency Mass Notification System & Mass Notification Software: What Are They?
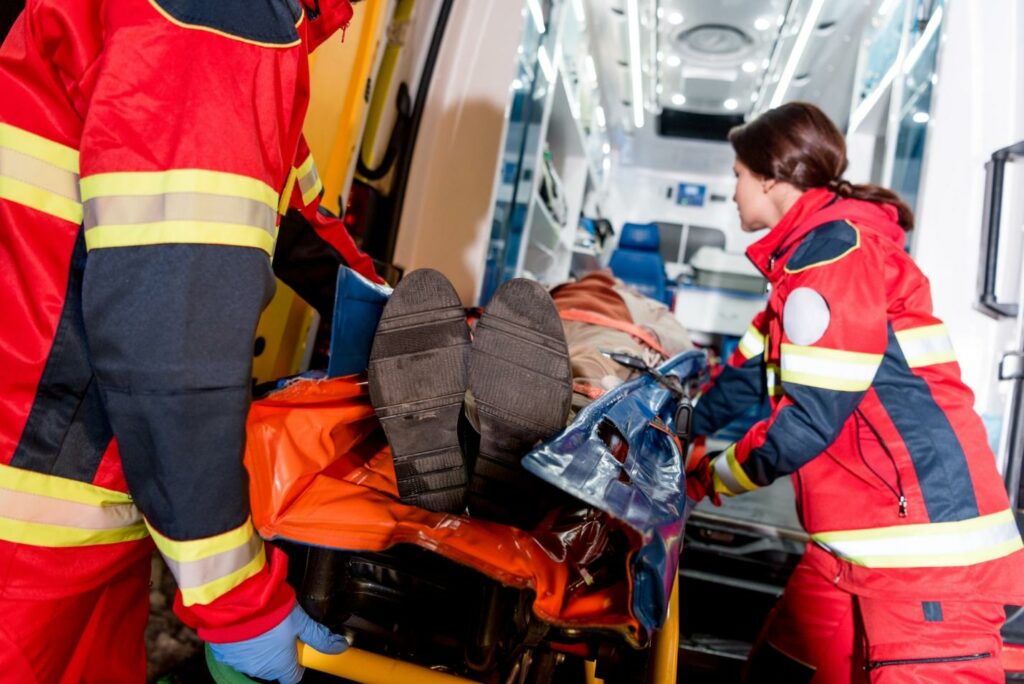

Companies should be able to quickly notify everyone when there’s some kind of threat out there. An entire team should be evacuated within minutes, regardless of whether they are in the basement or on the top floor.
Fortunately, this is now possible in today’s interconnected and fast-paced world. Traditional notifications are no longer enough, and radio broadcasts might not reach everyone. Fortunately, with the rise of remote employees or mobile ones that need to be out in the field, you can rely on an emergency mass notification system that’s going to be timely when it comes to sending messages and notifications to a lot of people simultaneously. This is often applicable in government settings, hospitals, schools, factories, and other institutions where there are a lot of people.
What’s an EMNS?
This is a platform that can rapidly send out messages during emergencies through push notifications, texts, voice calls, digital signs, social media pages, or desktop alerts. Below is an overview of how they work and the features that are typically involved with them:
They are often reliable in sending alerts that are user-created and they can be available in various settings. This means that employees or people involved can get notifications through their phones or a public address system when there’s a need.
Messages are often sent through a lot of communication channels, and this is not limited to one phone call. Instead, it can be insistent, especially if the level of the emergency is grave. The right emergency mass notification system & software can be installed in warehouses and other manufacturing facilities. They can also be a part of the company’s safety protocols where any announcements are broadcast through the audio systems for a more comprehensive approach, especially during an emergency.
Also, some systems allow for targeted messaging based on geographical locations. This feature ensures that only individuals in affected areas receive relevant alerts, reducing unnecessary panic or confusion, and this is often very helpful for a lot of people.
Another plus side is that the EMNS can integrate with other systems, such as weather monitoring so that snowstorms and hurricanes can be detected. They are automatically triggered based on the criteria and preferences set by the administration, and they can be helpful if there are instances of security threats that need to be addressed as soon as possible.
Advanced systems may include features for two-way communication, allowing recipients to respond to alerts, confirm their safety, request assistance, or provide additional information to emergency responders. Some users can customize messages for specific scenarios or use predefined templates for common emergencies like natural disasters, active shooter situations, or evacuation procedures.
The best EMNS can provide reporting and analytics tools to track message delivery, response rates, and other relevant metrics. Information like this can help organizations evaluate the effectiveness of their emergency communication strategies and make improvements as needed.
Accessibility for individuals with disabilities is also very important when implementing this kind of system. EMNS should support alternative formats, such as text-to-speech for the visually impaired and provide options for receiving alerts in multiple languages.
Software must be secure and reliable to maintain trust in the system. This includes measures to prevent unauthorized access, encryption of sensitive data, and redundancy to ensure continued operation during network outages or other disruptions. Finally, companies should provide training on how to use the EMNS effectively and conduct regular drills and tests to ensure that both staff and the general public are familiar with the system and know how to respond to alerts.
How to Find the Right Program?
Finding the best Emergency Mass Notification System or Mass Notification Software for your organization requires careful consideration of several factors. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you identify the most suitable solution:
Assess Your Needs
Start by identifying your organization’s specific requirements and objectives for an EMNS, which you can know more on this site. Consider factors such as the size of your organization, the number of people you need to reach, the types of emergencies you may encounter, and any regulatory compliance requirements relevant to your industry.
Research Providers
Look for reputable EMNS providers with a track record of delivering reliable and effective solutions. You can start by researching online, reading feedbacks, and asking for recommendations from industry peers or professional networks.
Evaluate Features and Functionality
Create a list of must-have features based on your organization’s needs. Consider factors such as multi-channel delivery options, geotargeting capabilities, integration with existing systems, two-way communication features, accessibility options, security measures, and reporting and analytics capabilities.
Request Demos and Trials
Reach out to shortlisted EMNS providers to schedule demos or request trial accounts. This will allow you to get hands-on experience with the software and evaluate its usability, user interface, and overall performance.
See information about software at this link: https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/definition/system-software.
Check References and Case Studies
Ask potential providers for references or case studies from organizations similar to yours that have implemented their EMNS. Contact these references to learn about their experiences with the software, including any strengths or weaknesses they’ve observed.
Consider Integration
If your organization already uses other emergency management or communication systems, consider how well the EMNS integrates with these existing platforms. Seamless integration can streamline workflows and improve overall efficiency.
Assess Support and Training Options
Evaluate the level of customer support and training resources offered by each provider.

Ensure that they provide comprehensive training for administrators and end-users and offer responsive technical support in case of issues or emergencies.
Evaluate Pricing and Contracts
Consider your budget constraints and carefully analyze the pricing plans and contract terms offered by each provider. Pay attention to factors such as subscription fees, implementation costs, additional charges for premium features or support, and contract duration.
Conduct Pilot Testing
If possible, conduct an initial assessment of the EMNS with a small group of users within your organization before committing to a full deployment. This will allow you to identify any potential issues or areas for improvement before rolling out the system to a larger audience.

 QR Codes and the Technology Driving Smarter Customer Journeys
QR Codes and the Technology Driving Smarter Customer Journeys  If AI Is the New Search Engine, Your Content Needs to Evolve
If AI Is the New Search Engine, Your Content Needs to Evolve  How Much Does Minecraft for Nintendo Switch Cost and What’s Included
How Much Does Minecraft for Nintendo Switch Cost and What’s Included